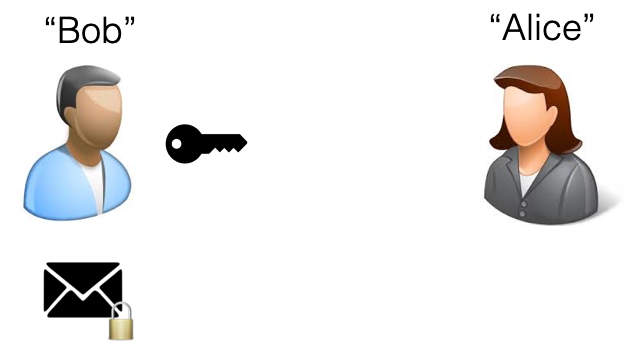Last time I finished up with a tremendously simplistic run through of how digital encryption uses certificates to create chains of proof that computers can use to establish trust in the identities of services and other computers they’re talking to. Still, certificates are only part of the deal, and you can’t have Public Key Infrastructure without, well, keys.
Remember Public Key Infrastructure? The thing that I made a fuss about and then said I wasn’t going to explain what it was until next time? Well, this is next time, so here goes.
To understand how PKI works it’s important to revisit symmetric encryption and talk about asymmetric encryption.
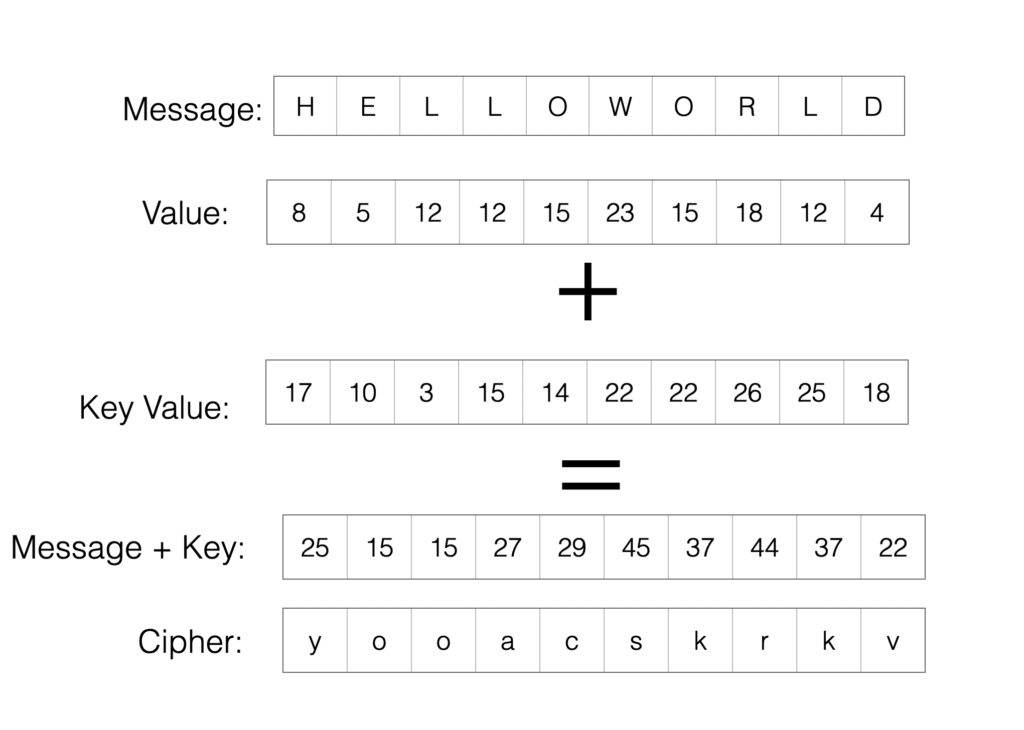
If symmetric encryption is using one key to encode and decode a piece of information then asymmetric encryption is the use of two keys to do the same. The two keys are a public key and a private key, and while in the real world you’d have one key that both locks and unlocks a door, you can think of these two keys as special keys that can only lock or unlock a door.
Let’s say that I run Big Dave’s Taco Shack™. In this example I’ve taken leave of my senses, thrown all my computer stuff into a hole in the ground and immediately embraced all my desires to become a terrible restauranteur. I go and sign a lease on a restaurant in a strip mall that nobody ever goes to, make a probably very politically and morally problematic sign to hang over the front door, then go and buy… I don’t know. Commercial taco-making apparatus, probably. This is a terrible example. Anyway, I also hire three people to work there – Jeff, Andy and Bob.
Jeff, Andy and Bob all close up the restaurant at the end of the night, and I give them a public key because locking the doors of my burgeoning taco enterprise so that it can’t be burglarized seems like a function that I’d want to make public – inasmuch as “public” means Jeff, Andy and Rob. The key that I give them can only be used to lock the door – if the door is locked and they put that special key into it and try and unlock it then it won’t work.
I’m the owner of this doomed culinary enterprise, and I don’t want anyone else to be able to get in there in the morning except me, so I have a special private key that only exists to unlock the door.
If Jeff, Andy and Bob leave their keys lying around then that’s actually okay, because nobody can use those keys to do anything except secure my fine dining establishment. Heck, I could just start handing out those keys to everyone I know or meet just in case they ever needed to lock my probably-failing-by-now eatery up safe and sound.
That’s how public and private keys work – one key (the public key, freely handed out to the world at large) cryptographically secures a piece of information or data, and the other (the private key, kept securely away from the public) cryptographically unlocks that piece of information or data.
Where to go from here.
There’s a lot more to dig into, here, and what I’ve laid out so far is an extremely simplified and high altitude view, tailored for people who’ve heard some of these terms and needed a broad explanation of what they mean. I’ve deliberately not touched on session keys, the mechanics of how digitally signing happens, signatures and hashes or even going through the anatomy of an SSL/TLS transaction works in the real world. When I had the idea for these articles I wanted to focus on the basic, basic mechanics of encryption and not obfuscate matters with a lot of more esoteric information, but there’s one final thing that I wanted to touch on…
You (or: Where It All Goes Horribly Wrong).
All right, maybe not you per se, but people. Historically, people have been the Achilles’ heel of security, because human beings are not reliable. They don’t work in absolute, finite and predictable ways, and they’re so far from infallible that it’s frankly laughable.
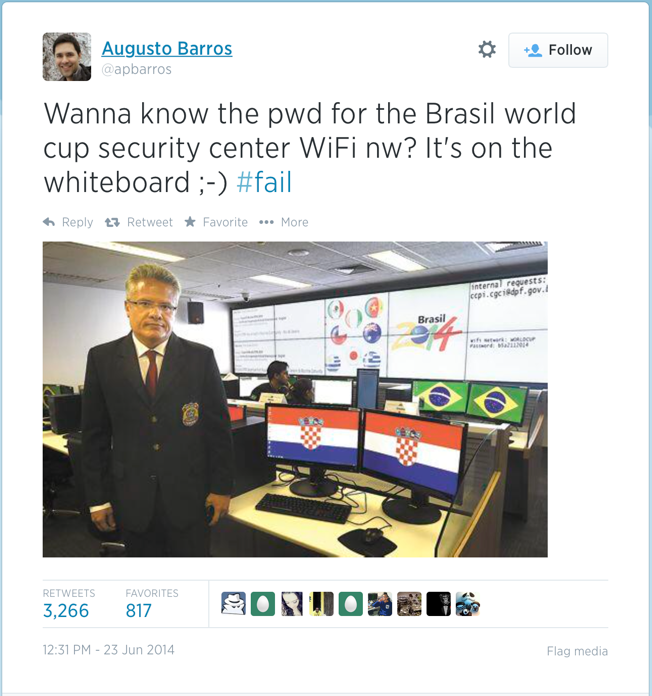
We’re careless. We leave passwords scrawled on post-it notes on our screens, or stuck underneath the keyboard and mouse mat. We use the same passwords for every service. We put together cryptographically secure wifi networks and write the password on a whiteboard and then have our photo taken of ourselves next to that whiteboard just like this chap during the Brazil World Cup:
Way back in the first article I wrote that Helen Keller quote about security, and I’ll throw it out there again:
“Security is mostly a superstition. It does not exist in nature.”
It’s an ugly truth, but nonetheless one that has to be carefully acknowledged. No matter how well-designed and cryptographically robust a security system you design or use, you can’t simply set it in place and rely on it to self-maintain. As a person who makes a living advising people on this kind of stuff it might seem self-serving to use this opportunity to do a hard sell on engaging professional help, but it’s nonetheless a good idea; still, there are some logical and fairly easy steps that you can take yourself.
• Be aware of PCI/HIPAA regulations, and talk with your credit card merchant (if you have one) and insurance company (again, if you have one) about their recommendations. These are entities that really, really don’t want you to have an expensive lapse in security and can probably direct you to resources that you’d find useful.
• Educate yourself. This little burst of articles about security and encryption were fun to write, but they in no way go into the kind of depth of information that’s out there (probably in better-written and more cogent form).
• Have good documentation about the products and services you’re using. I’m not suggesting writing down a list of passwords; rather it’s important to know what certificates and keys you’re using, who they’re authorized through and their expiration dates.
Above all, be vigilant and stay safe!